
Paragraph
REWRITER
Writing new content takes a lot of time and effort that requires careful attention to multiple factors. From citing multiple sources and structuring your writing to editing for clarity and revising before publication, each step demands precision.
And among all of these, you can easily tend to use your previous work without citing it. This leads to self plagiarism. This article breaks down what self plagiarism is and the best ways to avoid it.
Self plagiarism is the practice of reusing your own words from the work that is previously published without any proper citation. It is not as severe as using someone else’s content, but it can still create issues.
Let’s look at it this way: A professor assigns a new research paper and instead of writing fresh content, you submit multiple pieces from an old one you published in the previous semester. Or, as a blogger, you republish sections of an old article on a different platform without indicating that it was used before. It might not feel dishonest but it misleads readers and violates ethical writing standards.
In academic settings, self plagiarism can result in paper retractions and credibility loss.
Self-plagiarism isn’t just one-size-fits-all. It comes in different forms and each one can have consequences depending on the context. Whichever niche or department you’re in, recycling your own words without proper attribution can lead to ethical concerns. Here are the most common types and examples of self-plagiarism.
It is the practice of reusing portions of your previously published work without citing it. It’s not like outright copying, but since it involves repeating your own words across multiple publications, it can mislead readers into thinking it’s brand new content.
Example of text recycling: A researcher turns in a scientific publication, a paper. One year later, he turns in another work to another journal, copying whole passages from the last study without mentioning it.
Duplicate publication occurs when you submit or publish the same content in multiple places without disclosure. This is done to increase the reach and engagement of the published work. Why is it misleading? Because it ignores novelty and wastes editorial resources.
Example of duplicate publication: A content creator publishes an article on her website, then reposts it word-to-word on another site without indicating it’s a duplicate.
It is the practice of splitting a single study or research project into multiple smaller publications to increase publication count - just like you slice salamis to convert it from one to plenty.
Instead of presenting comprehensive findings in one paper, authors divide the data into fragmented studies without meaningful insights.
Example of salami slicing: A large-scale survey of consumer behavior is carried out by a financing company. They provide shorter reports, each focusing on a single tiny demographic category, rather than a single comprehensive report. Although it would increase downloads, industry professionals seeking comprehensive information would find it frustrating.
This form of self-plagiarism occurs when a student submits the same or slightly modified work for multiple courses or academic requirements without permission. This might seem like a time-saving shortcut (We know right?) but this practice violates academic integrity.
Example of self-duplication: A student writes an essay on “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health” for his Psychology class. Later, he submits the same paper in a Communications course without mentioning that it was used previously.
What is wrong with self-plagiarism? Well, we get it that it’s your work but it can be just as problematic as traditional plagiarism, especially in academic, research and professional settings.
Firstly, auto-plagiarism is a form of dishonesty. When you reuse old content without disclosure, it creates an illusion that it’s new and freshly researched even though it’s not.
Secondly, many universities and research institutions follow strict publication ethics and self-plagiarism is deemed as a violation of those guidelines. If a student submits the same paper for two different courses, or a researcher tries to publish the same study in multiple places, it could lead to outcomes like academic probation and paper retractions.
Thirdly, it chips away at that trust and damages your credibility. Trust, once broken, is hard to rebuild. If professionals engage in auto-plagiarism, they don’t just risk their reputation but also opportunities.
Now that you have understood the negative impact of auto-plagiarism, it’s time to discuss the next big question: How do you avoid self-plagiarism? Some of the most effective ways are mentioned below.
If you’re reusing ideas, data or text from your past publications, treat it the same way you would with external sources, i.e. cite it properly. There are many academic styles such as APA, MLA, and Chicago, through which you can cite your work. They are shown as follows:
APA style: Author name (Year). “Title of Research Paper.” Title of Journal, Volume (Issue), Page Numbers, DOI/URL (if applicable)
MLA style: Author name. “Title of Research Paper.” Title of Journal, vol. Volume no. Issue, Year, pp. Page numbers. DOI/URL (if applicable)
Chicago style: Author name, “Title of Research Paper.” Title of Journal Volume, no. Issue (Year): Page numbers. DOI/URL (if applicable)
In non-academic publications like content marketing articles, simply adding a note would suffice.
“This article expands on ideas from my previous work, ‘AI in Content Marketing (2021).”
One of the easiest ways to avoid self-plagiarism is by rewriting your content. This includes restructuring your sentences, using synonyms and changing the phrasing to make it feel like new content, but without changing the actual meaning of the text. Example?
Old: AI is transforming digital marketing by personalizing customer experiences.
Rewritten: With AI, digital marketing is evolving to deliver tailored experiences for customers.
Now, we get it – manual rewriting takes a lot of time. That’s where online rewriting tools like Paragraph Rewriter come in handy. Such AI-powered tools can help generate multiple variations of the same text while improving readability and refining the tone. Let's look at one example below:
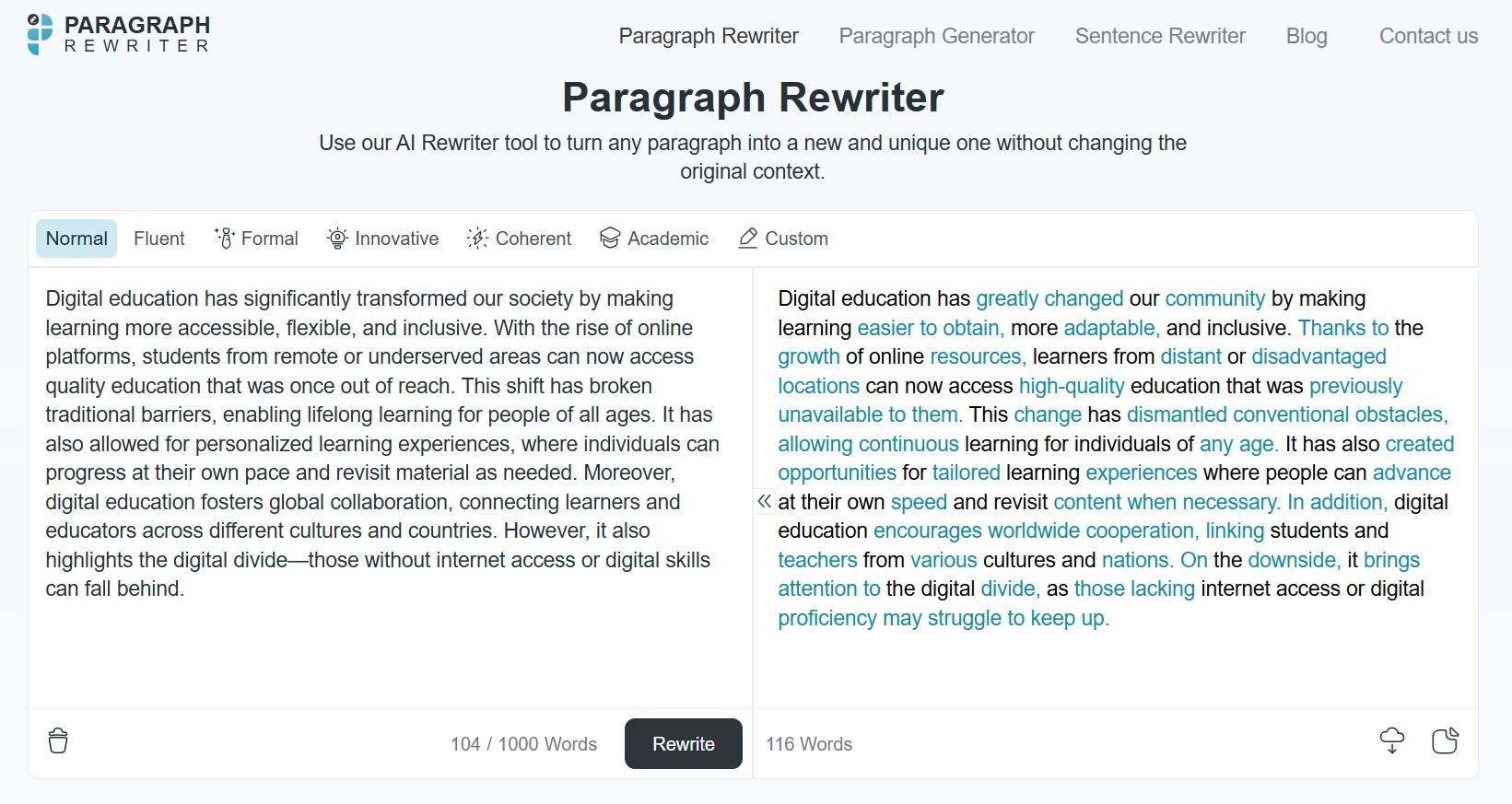
See, how refined the final output has become?
Even the most skilled writers can overlook self-plagiarism, which is why consulting with editors is a smart move. They ensure your work is original and properly cited.
In academic writing, you can take help from professors and journal editors. They can help you identify and improve sections that may unintentionally break academic integrity.
This is another effective method of prevention. Online plagiarism detectors help identify duplicate content and unintentional reuse so you can make necessary changes before publishing. Popular tools include Copyscape and Turnitin.
Hope you understand now what self-plagiarism is and how to avoid it. Whether it is unintentional or purposeful, you should take action to eliminate it in order to avoid the bad consequences. Respect your work, follow best practices and keep your writing truly original!